Research and collaboration#
Scalable computing hubs are designed to let researchers and data scientists leverage cloud infrastructure to facilitate collaboration and interactive computation. They are heavily inspired by the Pangeo Community infrastructure.
A brief overview of scalable computing hubs#
This hub deployment is designed for researchers and teams that wish to do their work in the cloud, and may need access to large-scale datasets and scalable computing.
Below is a diagram that showcases some of the major components of this hub:
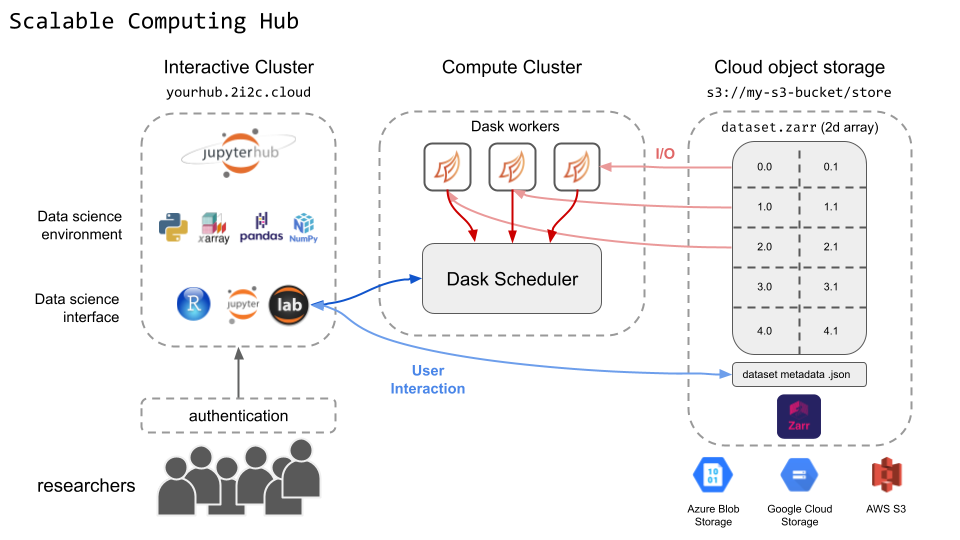
Fig. 3 A high level overview of major components in a scalable computing hub.#
And here are a few major aspects of these distributions:
The user environment: In addition, scalable computing is provided via dask and dask-gateway, which allows you to quickly scale computing resources as needed.
Environment
: Runs the pangeo-notebook Docker image.
This includes packages such as xarray, zarr, intake, and dask, along with the PyData stack.
However, you may also create your own environment image for your community.
Cloud infrastructure : The interactive computing environments for this hub should have more resources by default, and may be configured by the Hub Administrator to the appropriate levels depending on the kind of analysis being done. In addition, these hubs also deploy a scalable dask gateway cluster that allows users to leverage scalable computing to analyze data more quickly.
Cloud data : It is common for communities to use this hub in conjunction with cloud-native datasets that are in a parallel read/write-friendly format like the Zarr format. These hubs can be configured to have authenticated access to cloud datasets so that users can share access to the same data.
Interfaces : This hub comes with both JupyterLab, Jupyter Notebook, and RStudio interfaces by default.
A common workflow#
Below is a common workflow that communities use with this type of hub:
Store data in cloud-native format with Zarr. Communities store their data in the cloud in the Zarr format, and 2i2c runs the JupyterHub in the cloud provider where this data is located in order to minimize data egress fees.
Use Intake, Xarray, and JupyterLab for interactive exploration. Intake and Xarray allow you to quickly load and manipulate large-scale n-dimensional datasets in the cloud. Communities use these to do the quick “exploration and early analysis” work for their data.
Use Dask and Dask Gateway to scale compute. When you need to run an analysis on a larger dataset, use Dask and Dask Gateway to parallelize your computations in a cloud-efficient manner.
Inspiration for this hub#
The base infrastructure for this hub is largely inspired by the Pangeo Project, a community platform for Big Data geoscience. This platform is one of the cutting-edge workflows in cloud-native data science with large datasets, and drives development of a number of open source tools in this space. 2i2c helps the Pangeo Project run their infrastructure (more information here), and uses this as inspiration to fuel open source development in the PyData community.
